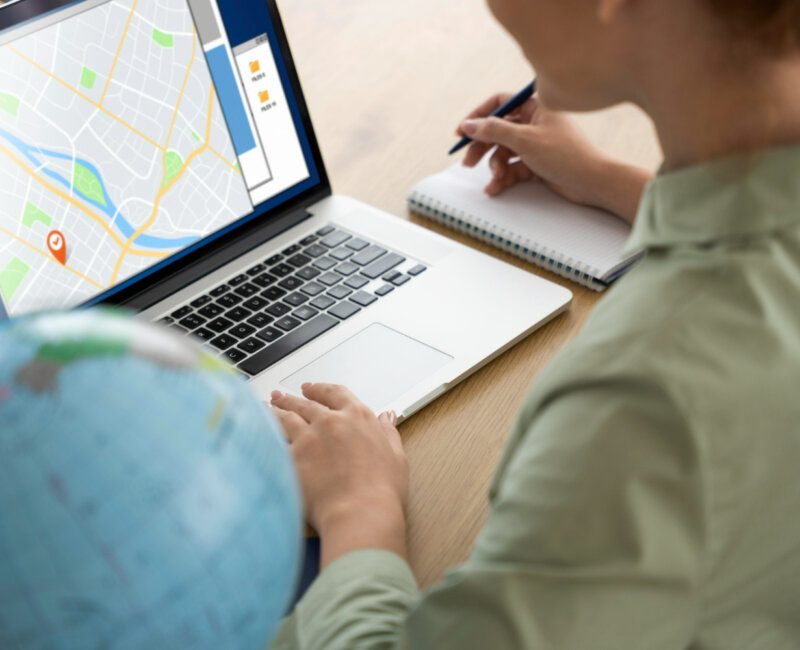
In an era where data has become the foundation of company strategy, the capacity to visualise and interpret information geographically has emerged as a game changer. Geo-mapping, or the process of creating visual representations of data on maps, enables businesses to get useful insights that can drive decision-making, optimise operations, and improve customer experiences. This article discusses the importance of geo-mapping, its uses, and how corporations may use this powerful tool to achieve strategic objectives.
The Significance of Geo-Mapping
Geo-mapping bridges the gap between data and location, enabling businesses to understand not just the ‘what’ but the ‘where’ of their data. This spatial awareness is crucial in today’s data-driven world for several reasons:
- Enhanced Data Visualisation: Geo-mapping provides a visual context that can make complex data sets more comprehensible. By representing data in a geographical format, organisations can identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that may not be apparent in traditional data presentations, such as spreadsheets or charts.
- Informed Decision-Making: When data is contextualised geographically, it allows leaders to make more informed decisions. For instance, a retailer can analyse foot traffic patterns to determine the best location for a new store, or a logistics company can optimise delivery routes based on real-time traffic data.
- Improved Customer Insights: Understanding customer demographics and behaviours through geo-mapping can lead to more effective marketing strategies. Businesses can tailor their offerings based on the preferences and needs of specific geographical segments, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Applications of Geo-Mapping Across Industries
The versatility of geo-mapping enables its application across a myriad of sectors, each reaping the benefits of spatial analysis:
- Retail: Retailers utilise geo-mapping to analyse customer demographics, shopping habits, and competition. This information can guide decisions on store locations, marketing campaigns, and inventory management.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, geo-mapping can identify health trends and disease outbreaks in specific areas. By visualising patient data geographically, healthcare providers can allocate resources more effectively and improve community health outcomes.
- Urban Planning: City planners employ geo-mapping to analyse land use, population density, and infrastructure needs. This data-driven approach facilitates better urban development and resource allocation, ultimately improving the quality of life for residents.
- Agriculture: Farmers can leverage geo-mapping for precision agriculture, enabling them to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This information can lead to more efficient farming practices and increased yields.
- Emergency Management: Geo-mapping plays a critical role in disaster response and management. By mapping natural disaster risks and resources, emergency services can develop effective response strategies to safeguard communities.
How to Leverage Geo-Mapping for Business Success
To harness the power of geo-mapping, businesses must adopt a strategic approach:
- Invest in Technology: Modern geo-mapping relies on sophisticated software and tools that can analyse and visualise data effectively. Investing in the right technology, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), can significantly enhance a company’s geo-mapping capabilities.
- Integrate Data Sources: For geo-mapping to yield actionable insights, organisations must integrate various data sources. This could include customer databases, sales data, social media analytics, and environmental data, providing a holistic view of the business landscape.
- Train Employees: Ensuring that employees are skilled in geo-mapping tools and techniques is vital. Training programmes can equip staff with the necessary knowledge to analyse and interpret geo-mapped data effectively.
- Encourage Collaboration: Cross-departmental collaboration can foster a culture of data-driven decision-making. By involving various teams in the geo-mapping process, businesses can leverage diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Stay Updated: The field of geo-mapping is continually evolving, with advancements in technology and data analysis techniques. Staying abreast of these developments can help businesses remain competitive and make the most of geo-mapping tools.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Geo-Mapping
Several organisations have successfully implemented geo-mapping to drive their business strategies:
Starbucks
The coffee giant uses geo-mapping to analyse customer demographics and preferences. By visualising data on a map, Starbucks can identify optimal locations for new stores, ensuring they meet consumer demand effectively.
Walmart
Walmart employs geo-mapping to optimise its supply chain and distribution networks. By analysing geographic data on sales patterns and customer locations, the retail behemoth enhances its inventory management and delivery processes.
Uber
Uber leverages geo-mapping to improve its ride-hailing services. By analysing real-time data on passenger requests and traffic patterns, Uber can optimise driver routes, reducing wait times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Unlocking the power of geo-mapping presents a wealth of opportunities for organisations across various sectors. By transforming data into actionable insights, businesses can enhance their decision-making processes, improve customer experiences, and optimise operations. As the technology continues to evolve, the potential of geo-mapping will only expand, making it an indispensable tool in the modern data landscape. Embracing this powerful resource can set the stage for sustained success in an increasingly competitive environment.









